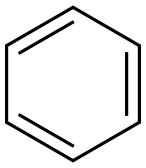
Benzene CAS 71-43-2
Chemical Formula: C₆H₆
Molecular Weight: 78.11 g/mol
CAS Number: 71-43-2
1. By Air, fast but expensive.
2. By Sea, usual and economy.
3. By Train, suit for middle Asia countries.
4. By Express, suit for small package.
We only provide highest quality goods available, accompanied by after support!
Product Description:
Benzene (C₆H₆) is a widely used aromatic hydrocarbon with a colorless, highly flammable liquid form and a sweet odor. It is an essential raw material in the chemical industry, particularly in the production of polymers, synthetic fibers, rubber, and various other chemicals. Benzene is a building block for a variety of derivatives like styrene, phenol, cyclohexane, and other industrial chemicals.
Chemical Properties:
Chemical Formula: C₆H₆
Molecular Weight: 78.11 g/mol
CAS Number: 71-43-2
IUPAC Name: Benzene
Synonyms: Benzol, Phenyl Hydride, Cyclohexatriene
Boiling Point: 80.1°C
Melting Point: 5.5°C
Density: 0.879 g/cm³ at 20°C
Vapor Pressure: 12.8 mmHg at 20°C
Solubility: Insoluble in water, soluble in organic solvents like alcohol, ether, and chloroform
Flash Point: -11°C (10°F) (closed cup)
Appearance: Colorless liquid with a sweet odor
Refractive Index: 1.501 at 20°C
Viscosity: 0.65 cP at 25°C
Evaporation Rate: 4.4 (butyl acetate = 1)
Physical Properties:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | C₆H₆ |
| Molecular Weight | 78.11 g/mol |
| Boiling Point | 80.1°C |
| Melting Point | 5.5°C |
| Density | 0.879 g/cm³ at 20°C |
| Solubility | Insoluble in water |
| Vapor Pressure | 12.8 mmHg at 20°C |
| Flash Point | -11°C (closed cup) |
| Refractive Index | 1.501 at 20°C |
| Viscosity | 0.65 cP at 25°C |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
Chemical Reactions:
Benzene is highly stable, but it reacts under specific conditions, such as high temperatures or the presence of catalysts. Common reactions include:
Electrophilic Substitution Reactions:
Halogenation: Benzene reacts with halogens like chlorine or bromine in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst (FeCl₃, AlCl₃).
Nitration: Reaction with concentrated nitric acid (HNO₃) and sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) to form nitrobenzene.
Sulfonation: Reaction with concentrated sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) to form benzene sulfonic acid.
Polymerization:
Benzene is used in polymerization reactions to form various plastics and synthetic rubbers like polystyrene and synthetic rubber.
Applications of Benzene:
Chemical Manufacturing:
Styrene Production: Benzene is the precursor to styrene, used in the production of polystyrene, ABS plastic, and synthetic rubber.
Phenol Production: Benzene is also used in the production of phenol, which is a key ingredient in plastics, resins, and adhesives.
Cyclohexane: Used in the production of nylon and other synthetic fibers.
Caprolactam: Benzene is a raw material for the manufacture of caprolactam, which is used in nylon-6 production.
Solvent:
Due to its solvent properties, benzene is widely used in laboratories and industries for dissolving oils, resins, and other substances. However, its use as a solvent is being phased out in favor of less toxic alternatives due to its carcinogenic nature.
Pharmaceuticals:
Benzene is used in the synthesis of various pharmaceutical products and intermediates.
Rubber Manufacturing:
Benzene is used in the production of synthetic rubber (butadiene), which is used in tires and other rubber products.
Paints and Coatings:
Used as a solvent in the formulation of paints, coatings, varnishes, and lacquers.
Health and Safety Considerations:
Benzene is classified as a carcinogen by various health organizations, including the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Long-term exposure can lead to severe health risks, including leukemia, bone marrow suppression, and other health complications. Proper protective measures should be taken when handling benzene, such as:
Wearing gloves and protective clothing
Using proper ventilation systems
Avoiding direct inhalation of vapors
Packaging and Storage:
Packaging: Benzene is typically packaged in steel drums or bulk containers (ISO tanks or tanker trucks) depending on the volume and client requirements.
Storage: Store in a cool, dry place away from heat, sparks, and open flames. Keep in tightly sealed containers and store away from oxidizing agents, acids, and other reactive substances.
Handling: Use proper equipment and precautions to avoid exposure, as benzene is toxic and carcinogenic.
Product Specifications:
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | C₆H₆ |
| CAS Number | 71-43-2 |
| Purity | ≥99.9% |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Boiling Point | 80.1°C |
| Melting Point | 5.5°C |
| Density | 0.879 g/cm³ |
| Flash Point | -11°C (closed cup) |
| Solubility | Insoluble in water |
| Viscosity | 0.65 cP at 25°C |
| Packaging | 180kg/Drum, 1000kg/IBC, or bulk tanker |
Factory and Equipment Show


Fast transport time
Inventory 2-3 working days New manufacturing 7-10 working days