Tetrahydrothiophene CAS#110-01-0
Tetrahydrothiophene CAS#110-01-0 Promotion Season Now in Store and Free Sample for Testing with Factory Price
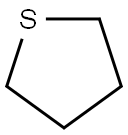
Chemical Name:Tetrahydrothiophene
CAS No.: 110-01-0
Molecular Formula:C4H8S
Molecular weight:88.17
Sample: Available
Mode of Transportation
1. By Air, fast but expensive.
2. By Sea, usual and economy.
3. By Train, suit for middle Asia countries.
4. By Express, suit for small package.
We only provide highest quality goods available, accompanied by after support!
Products Description of Tetrahydrothiophene CAS#110-01-0
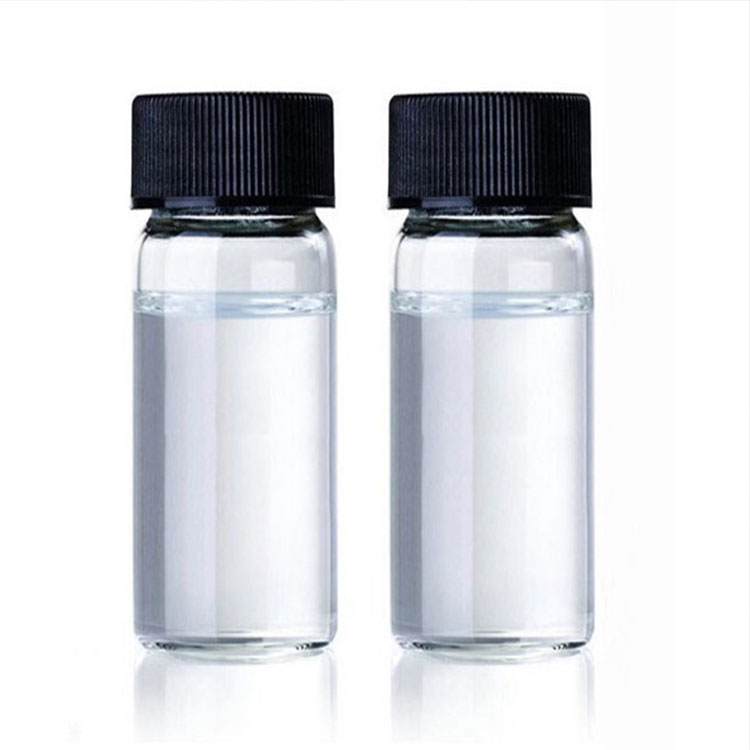
Tetrahydrothiophene (abbreviated as THT), also known as thiolane, tetramethylene sulfide, butyl sulfide, tetrahydrothiophene, is a sulfur-containing saturated heterocyclic compound obtained by catalytic hydrogenation of thiophene. After thiophene is reduced to tetrahydrothiophene, it no longer has a conjugated system and aromaticity. Therefore, tetrahydrothiophene shows the properties of general sulfides and is easily oxidized to sulfoxides and sulfones (cyclopentane sulfone). Tetrahydrothiophene is a colorless, transparent, volatile liquid that is insoluble in water and miscible in ethanol, ether, benzene, and acetone. It has a strong unpleasant odor. The odor it produces is stable and not easy to dissipate. It can be smelled when it exists in the air at 0.01 PPm. It is not corrosive to materials such as gas equipment and transportation pipeline gaskets, and does not produce habitual passivation to the human sense of smell. Therefore, it is used as a leakage warning agent for gas fuels such as city gas and natural gas. It is added to gas fuels in small quantities to replace the original odorizers such as ethyl mercaptan. At present, the domestic market requires about 400 tons of tetrahydrothiophene per year, which mainly relies on imports. Tetrahydrothiophene has an anesthetic effect. When mice inhale poisoning, they experience motor excitement, ataxia, anesthesia, and finally death. In chronic poisoning experiments, mice show abnormal behavior, stagnation of weight gain, and changes in liver function. In addition, it is also used as medicine, pesticide, and organic synthesis raw material.
Tetrahydrothiophene Chemical Properties
Melting point | -96 °C (lit.) |
Boiling point | 119 °C (lit.) |
density | 1 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
vapor pressure | 18 mm Hg ( 25 °C) |
refractive index | n20/D 1.504(lit.) |
Fp | 55 °F |
storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
solubility | immiscible |
form | liquid |
Specific Gravity | 1.002 (20/4℃) |
color | Colorless to Almost colorless |
Odor | Smells of rotting eggs |
PH | 7 (H2O, 20℃) |
explosive limit | 1.1-12.1%(V) |
Odor Threshold | 0.00062ppm |
Odor Type | sulfurous |
Water Solubility | immiscible |
Merck | 14,9218 |
BRN | 102392 |
Dielectric constant | 8.6099999999999994 |
Stability: | Highly flammable. Vapour-air mixtures explosive in some proportions; note low flash point and fairly wide explosion limit range. Heavier than air, so potentially explosive mixtures may travel considerable distances to source of ignition. |
LogP | 1.8 at 20℃ |
CAS DataBase Reference | 110-01-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
NIST Chemistry Reference | Thiophene, tetrahydro-(110-01-0) |
EPA Substance Registry System | Tetrahydrothiophene (110-01-0) |
Safety Information
Hazard Codes | F,Xn |
Risk Statements | 11-20/21/22-36/38-52/53 |
Safety Statements | 16-23-36/37-61 |
RIDADR | UN 2412 3/PG 2 |
WGK Germany | 2 |
RTECS | XN0370000 |
Autoignition Temperature | 202 °C |
TSCA | Yes |
HazardClass | 3 |
PackingGroup | II |
HS Code | 29349990 |
Hazardous Substances Data | 110-01-0(Hazardous Substances Data) |
Toxicity | LD50 by inhalation in mice: 26.7 mg/l (Carlucci) |
Product Application of Tetrahydrothiophene CAS#110-01-0
It is used as an odorant for fuel gases such as city gas, liquefied petroleum gas, and natural liquefied gas. It can also be used as a raw material for medicine and pesticides.
Factory and Equipment Show


Fast delivery time
Inventory 2-3 working days New production 7-10 working days