Phenol CAS# 108-95-2
Phenol CAS# 108-95-2 Promotion Season Now in Store and Free Sample for Testing with Factory Price
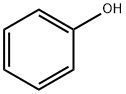
Chemical Name:Phenol
CAS No.:108-95-2
Molecular Formula:C6H6O
Molecular weight:94.11
Sample: Available
Mode of Transportation
1. By Air, fast but expensive.
2. By Sea, usual and economy.
3. By Train, suit for middle Asia countries.
4. By Express, suit for small package.
We only provide highest quality goods available, accompanied by after support!
Phenol CAS# 108-95-2
Phenol is the easiest member of a classification of natural compounds possessing a hydroxyl team connected to a benzene ring or to a extra complicated fragrant ring system.
Also recognized as carbolic acid or monohydroxybenzene, phenol is a colorless to white crystalline fabric of candy odor, having the composition C6H5OH, bought from the distillation of coal tar and as a derivative of coke ovens.
Phenol has extensive biocidal properties, and dilute aqueous options have lengthy been used as an antiseptic. At greater concentrations, it motives extreme pores and skin burns; it is a violent systemic poison. It is a precious chemical uncooked cloth for the manufacturing of plastics, dyes, pharmaceuticals, syntans, and different products.
phenol crystal
Phenol melts at about 43°C and boils at 183°C. The pure grades have melting factor of 39°C, 39.5°C, and 40°C. The technical grades include 82%-84% and 90%-92% phenol. The crystallization factor is given as 40.41°C. The unique gravity is 1.066. It dissolves in most natural solvents. By melting the crystals and including water, liquid phenol is produced, which stays liquid at regular temperatures. Phenol has the uncommon property of penetrating residing tissues and forming a treasured antiseptic. It is additionally used industrially in reducing oils and compounds and in tanneries. The cost of different disinfectants and antiseptics is generally measured by means of evaluation with phenol.

Phenol Chemical Properties |
Melting point | 40-42 °C(lit.) |
Boiling point | 182 °C(lit.) |
density | 1.071 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
vapor density | 3.24 (vs air) |
vapor pressure | 0.09 psi ( 55 °C) |
FEMA | 3223 | PHENOL |
refractive index | n |
Fp | 175 °F |
storage temp. | 2-8°C |
solubility | H2O: 50 mg/mL at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
form | liquid |
pka | 9.89(at 20℃) |
Specific Gravity | 1.071 |
color | faintly yellow |
PH | 6.47(1 mM solution);5.99(10 mM solution);5.49(100 mM solution); |
Odor | Sweet, medicinal odor detectable at 0.06 ppm |
Odor Threshold | 0.0056ppm |
explosive limit | 1.3-9.5%(V) |
Odor Type | phenolic |
Water Solubility | 8 g/100 mL |
FreezingPoint | 41℃ |
Sensitive | Air & Light Sensitive |
Merck | 14,7241 |
JECFA Number | 690 |
BRN | 969616 |
Henry's Law Constant | 1.09 at 5 °C (average derived from six field experiments, Lüttke and Levsen, 1997) |
Exposure limits | TLV-TWA skin 5 ppm (~19 mg/m3 ) (ACGIH, MSHA, and OSHA); 10-hour TWA 5.2 ppm (~20 mg/m3 ) (NIOSH); ceiling 60 mg (15 minutes) (NIOSH); IDLH 250 ppm (NIOSH). |
Dielectric constant | 4.3(10℃) |
Stability: | Hygroscopic |
InChIKey | ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
LogP | 1.47 at 30℃ |
CAS DataBase Reference | 108-95-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
IARC | 3 (Vol. 47, 71) 1999 |
NIST Chemistry Reference | Phenol(108-95-2) |
EPA Substance Registry System | Phenol (108-95-2) |
Safety Information |
Hazard Codes | T,C,F,Xn |
Risk Statements | 23/24/25-34-48/20/21/22-68-40-39/23/24/25-11-36-20/21/22-24/25 |
Safety Statements | 26-36/37/39-45-36/37-28A-28-24/25-1/2-36-16-7 |
RIDADR | UN 2821 6.1/PG 2 |
OEB | A |
OEL | TWA: 5 ppm (19 mg/m3), Ceiling: 15.6 ppm (60 mg/m3) [15-minute] [skin] |
WGK Germany | 2 |
RTECS | SJ3325000 |
F | 8-23 |
Autoignition Temperature | 715 °C |
TSCA | Yes |
HazardClass | 6.1 |
PackingGroup | II |
HS Code | 29071100 |
Hazardous Substances Data | 108-95-2(Hazardous Substances Data) |
Toxicity | LD50 orally in rats: 530 mg/kg (Deichmann, Witherup) |
IDLA | 250 ppm |
Product Usage
Propionic acid is used in the productionof propionates used as mold inhibitors andpreservatives for grains and wood chips, inthe manufacture of fruit flavors and perfumebases, and as an esterifying agent.
Propionic Acid is the acid source of the propionates. propionic acid in the liquid form has a strong odor and is corrosive, so it is used as the sodium, calcium, and potassium salts as a preservative. these yield the free acid in the ph range of the food in which they are used. it functions principally against mold.
Factory and Equipment Show


Fast transport time
Inventory 2-3 working days New manufacturing 7-10 working days