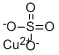Copper(II) sulfate CAS#7758-98-7
Copper(II) sulfate CAS#7758-98-7 Promotion Season Now in Store and Free Sample for Testing with Factory Price
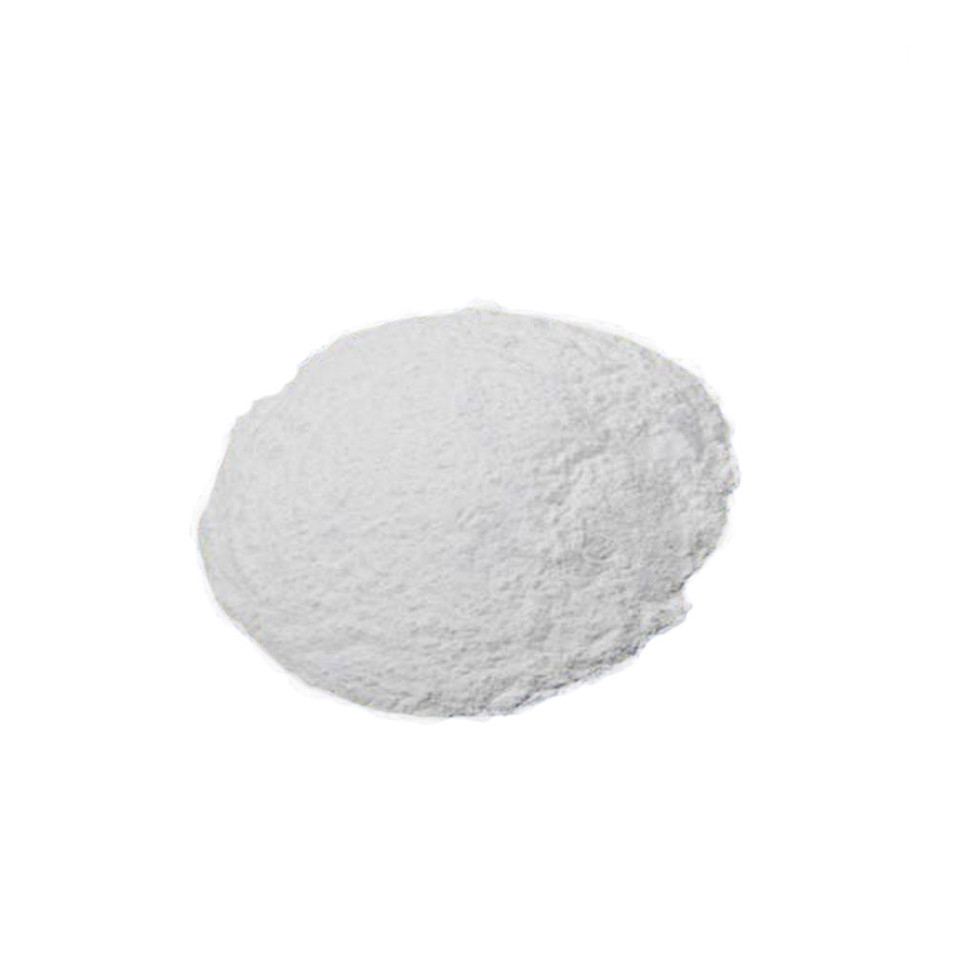
Chemical Name:Copper(II) sulfate
CAS No.:7758-98-7
Molecular Formula:CuO4S
Molecular weight:159.61
Sample: Available
Mode of Transportation
1. By Air, fast but expensive.
2. By Sea, usual and economy.
3. By Train, suit for middle Asia countries.
4. By Express, suit for small package.
We only provide highest quality goods available, accompanied by after support!
Products Description of Copper(II) sulfate CAS#7758-98-7
Copper sulfate is an inorganic compound. The inorganic industry uses it to make other copper salts such as cuprous chloride, cupric chloride, copper pyrophosphate, cuprous oxide, copper acetate, copper carbonate, etc. The common form of copper sulfate is crystals. Anhydrous copper sulfate is a white crystalline powder, which may also be light gray-green due to impurities. It is a soluble copper salt. The relative density is 3.603, and the solubility in water at 25°C is 23.05g. It is insoluble in ethanol and ether, but easily soluble in water. The aqueous solution is blue. It is a strong acid and weak base salt. The hydrolyzed solution is weakly acidic and has a strong ability to kill pathogens.
It is widely used in the prevention and treatment of fish diseases in aquaculture. The solution is concentrated and crystallized to obtain blue crystals of copper sulfate pentahydrate, commonly known as gallstone, stone gall, copper sulfate or blue sulfate. It is toxic, odorless, and has a metallic astringent taste. It is very stable at room temperature and pressure, does not deliquesce, and will gradually weather in dry air. When heated to 45°C, it loses two molecules of crystal water, loses four molecules of crystal water at 110°C, and loses all crystal water at 150°C to become anhydrous (water absorption can be converted into gallstone). At 650°C, it decomposes into copper oxide and sulfur trioxide. The copper sulfate aqueous solution appears blue due to the hydrated copper ions. This property is often used in the laboratory to test the presence of water. In real production and life, it is often used to refine refined copper, and mixed with slaked lime to make Bordeaux mixture, a pesticide. The copper ions in copper sulfate can destroy the three-dimensional structure of protein and denature it. When measuring protein concentration, alkali is often added to the protein, and then copper sulfate solution is added. At this time, the solution will turn purple. This reaction is called biuret reaction. Copper sulfate is a heavy metal salt, which is toxic. The lethal dose for adults is 0.9g/kg. If ingested by mistake, you should immediately consume large amounts of protein-rich foods such as milk and egg white, or use EDTA calcium sodium salt to detoxify.
Copper(II) sulfate Chemical Properties
Melting point | 200 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
density | 3.603 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
vapor pressure | 7.3 mm Hg ( 25 °C) |
storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
solubility | H2O: soluble |
form | powder |
Specific Gravity | 3.603 |
color | Slightly greenish to gray |
PH | 3.5-4.5 (50g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
Odor | odorless |
PH Range | 3.7 - 4.5 |
Water Solubility | 203 g/L (20 ºC) |
Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
Merck | 14,2653 |
Dielectric constant | 10.3(0.0℃) |
Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 1 mg/m3 |
Stability: | hygroscopic |
InChIKey | ARUVKPQLZAKDPS-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
CAS DataBase Reference | 7758-98-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
NIST Chemistry Reference | Cupric sulfate(7758-98-7) |
EPA Substance Registry System | Cupric sulfate (7758-98-7) |
Safety Information
Hazard Codes | Xn,N,Xi |
Risk Statements | 36/38-50/53-22-51/53-36/37/38 |
Safety Statements | 24/25-36-60-61-22-26 |
RIDADR | UN 3288 6.1/PG 3 |
WGK Germany | 2 |
RTECS | GL8800000 |
F | 3 |
TSCA | Yes |
HS Code | 2833 25 00 |
HazardClass | 6.1 |
PackingGroup | III |
Hazardous Substances Data | 7758-98-7(Hazardous Substances Data) |
Toxicity | LD50 orally in Rabbit: 481 mg/kg |
Product Application of Copper(II) sulfate CAS#7758-98-7
Copper sulfate can be used to kill fungi. When mixed with lime water, it forms Bordeaux mixture, which is used to control fungi on crops such as lemons and grapes. Dilute solutions are used to sterilize aquariums and remove snails. Since copper ions are toxic to fish, the dosage must be strictly controlled. Most fungi can be killed with very low concentrations of copper sulfate.
In addition, copper sulfate can also be used to control Escherichia coli. Aqueous solution of ketone sulfate has a strong bactericidal effect. It is mainly used in agriculture to prevent and control various diseases such as fruit trees, malt, potatoes, and rice, with good results, but has poor effects on rust and powdery mildew. At the same time, it causes phytotoxicity to plants, and is only used on crops with strong tolerance to copper ion phytotoxicity or on fruit trees in dormancy.
It is a preventive fungicide that needs to be used before the disease occurs. It can also be used to remove algae in rice fields and ponds. It is also a trace element fertilizer that can improve the stability of chlorophyll, prevent chlorophyll from being destroyed prematurely, and promote crop absorption. Crops will lose their green color when they lack copper. When fruit trees lack copper, the fruits will be small and the flesh will become hard. In severe cases, the fruit trees will die. Crops that are sensitive to copper are cereals such as wheat, barley, oats, etc. It is mainly used for seed treatment and foliar fertilization.
Factory and Equipment Show


Fast delivery time
Inventory 2-3 working days New production 7-10 working days